What Is Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
September 23, 2025
Best GRC Tools 2025 for Your Business
September 23, 2025MFA vs 2FA Differences Examples and Which Is More Secure
Introduction
Digital security is increasingly important in today’s complex cyber threat landscape. Two common authentication methods often discussed are 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) and MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication). While they may look similar at first, there are significant differences. This article explores MFA vs 2FA in detail, including examples, benefits, and when each should be used.
If you want to understand the basics of IAM first, check our earlier article:
Multifactor Authentication: Definition, How It Works, and Benefits
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
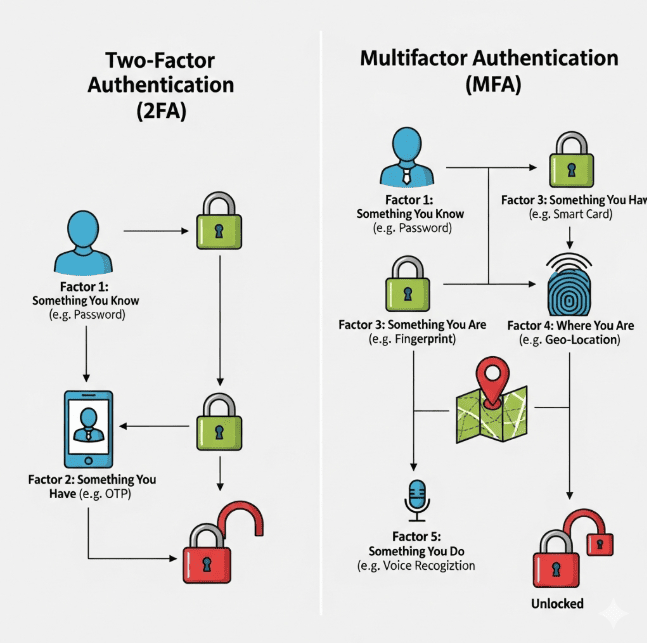
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a method that requires two factors to verify a user’s identity. Typically a combination of:
- Something you know → a password or PIN.
- Something you have → an OTP code from SMS, email, or authenticator app.
Example of 2FA: A user logs into their email with a password, then is prompted to enter an OTP code from Google Authenticator.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) requires two or more verification factors. In fact, 2FA is considered a subset of MFA.
Beyond knowledge and possession, MFA can also include:
- Something you are → biometrics like fingerprint, face, or voice recognition.
- Contextual/adaptive factors → location, device, or network used.
Example of MFA: A banking app login requires a password, push notification approval on a phone, and fingerprint verification.
| Aspect | 2FA | MFA |
|---|---|---|
| Number of factors | Always two | Two or more |
| Common example | Password + OTP | Password + OTP + biometric |
| Security | Safer than single factor, but limited | Stronger with multiple layers |
| Complexity | Simple and easy to use | More complex, may add login steps |
| Best suited for | Individual users, standard apps | Large organizations, sensitive data, regulated sectors |
Benefits of MFA and 2FA
Benefits of 2FA
- Improves security compared to password-only login.
- Easy to implement with low cost.
- Suitable for individuals or small businesses.
Shared Benefits of 2FA and MFA
- Stronger protection for sensitive data.
- Supports compliance with security standards and regulations (e.g., finance, healthcare).
- Harder to bypass because it requires multiple factors.
Challenges of Implementing 2FA and MFA
- 2FA → relatively simple, but if the second factor is SMS OTP only, it remains vulnerable to SIM swap or phishing attacks.
- MFA → more secure, but adds steps that may frustrate users. Implementation costs are also higher.
When Should Businesses Use 2FA or MFA
- Use 2FA when you need basic extra security for personal accounts or non-critical apps.
- Use MFA when protecting sensitive data such as banking, healthcare, government services, or enterprise applications.
Conclusion
MFA vs 2FA are often confused, but there are important distinctions. 2FA always requires two factors, while MFA can involve two or more. For individuals or small businesses, 2FA provides sufficient security. However, for large organizations handling sensitive data, MFA is the best choice due to its stronger layers of protection.
For more details, check CyberHub on 2FA vs MFA or UpGuard’s explanation of 2FA vs MFA.